Major insights about Sugar beet vs sugar cane taste vs. health
Wiki Article
Introducing the Fact Behind Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Advantages, Makes Use Of, and Handling Techniques Clarified
The distinction in between sugar beet and sugar cane is frequently neglected in discussions about sugar manufacturing. Each crop presents special benefits and applications in various markets. Their cultivation techniques and handling techniques additionally vary significantly. Understanding these nuances is essential for stakeholders in the sugar market. What implications do these distinctions have for health, flavor, and ecological influence? Discovering these elements can disclose deeper understandings into the global sugar market.
Introduction of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 main sources of sugar, each with unique features and growing methods. Sugar beet, a root veggie, thrives in temperate climates and is commonly gathered in the autumn. Its high sugar web content, varying from 15% to 20%, makes it an important plant for sugar manufacturing. The procedure entails removing juice from the beetroots, which is then refined right into granulated sugar.In comparison, sugar cane is an exotic turf that thrives in warm, moist environments. It can attain a sugar content of approximately 14%, yet its tall, fibrous stalks need considerable handling. The cane is crushed to draw out juice, which goes through boiling and condensation to create sugar. Both resources contribute substantially to the global sugar supply, with sugar beet mainly grown in Europe and The United States And Canada, while sugar cane is chiefly expanded in Brazil, India, and various other exotic regions.
Farming Practices: Sugar Beet vs. Sugar Cane
Cultivation methods for sugar beet and sugar cane vary substantially as a result of their distinct expanding problems. Sugar beetroots flourish in cooler environments with well-drained dirt, while sugar cane favors warmer temperatures and plentiful moisture. Additionally, the harvesting techniques used for each and every plant mirror these environmental demands and influence overall yield and top quality.Growing Conditions Contrast
While both sugar beet and sugar cane flourish in certain environmental conditions, their growing techniques vary considerably. Sugar beet is mainly expanded in temperate areas, preferring cooler environments with well-drained soil and modest rainfall. It requires a growing period of about 90 to 120 days, with excellent temperatures in between 15 ° C to 25 ° C. In comparison, sugar cane embellishments in tropical and subtropical climates, growing in cozy temperatures ranging from 20 ° C to 32 ° C. It needs plentiful sunshine and consistent rains, commonly requiring irrigation in drier locations. Sugar cane has a much longer growing cycle, commonly lasting 12 to 24 months. These differences in expanding conditions significantly influence the geographical circulation and agricultural practices linked with each crop.Gathering Techniques Distinctions
The harvesting methods for sugar beet and sugar cane show their distinctive growth characteristics and agricultural practices. Sugar beet is usually collected mechanically, with farmers created to root out the entire plant, making certain very little dirt disruption. The beetroots are after that moved for handling shortly after harvest to keep quality. In comparison, sugar cane harvesting usually involves a combination of manual and mechanical methods. Employees may at first reduce the cane by hand, specifically in areas where automation is less feasible. Consequently, specialized equipment is utilized to gather and transport the cut stalks to processing centers. These differing techniques not just effect effectiveness however also influence the quality and return of the last sugar products, showcasing the adaptability of each crop to its atmosphere.Nutritional Comparison and Health Advantages
When contrasting the dietary accounts of sugar beet and sugar cane, it ends up being clear that each deals unique health and wellness benefits. Sugar beets are rich in essential nutrients like folate, manganese, and potassium, which add to total wellness. They likewise have fiber, which assists digestion and might help manage blood glucose degrees. In addition, sugar beets are known for their antioxidant buildings, which can battle oxidative anxiety.On the other hand, sugar cane is primarily made up of sucrose, giving quick power. While it lacks the exact same level of minerals and vitamins discovered in sugar beets, sugar cane does consist of small quantities of B minerals and vitamins such as calcium and magnesium. Moreover, sugar cane juice is frequently proclaimed for its hydrating residential properties and potential health and wellness benefits, consisting of boosted digestion wellness. Eventually, the option between sugar beet and sugar cane may rely on specific wellness objectives and dietary choices.
Flavor Profiles and Culinary Utilizes
Flavor accounts of sugar beet and sugar cane vary noticeably, affecting their cooking applications (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Sugar cane, with its naturally wonderful and complicated taste, is frequently preferred in beverages, desserts, and various culinary recipes. It offers an abundant, caramel-like note that boosts the preference of products such as syrups, molasses, and rum. On the other hand, sugar beet has a more neutral and less fragrant preference, making it appropriate for applications where sweet taste is preferred without changing the dish's inherent tastes. It is frequently used in refined foods, baked items, and sweetenersCulinary experts usually select sugar cane for its deepness and richness, especially in exquisite cooking and craft drinks. On the other hand, sugar beet's versatility as a sweetener in mass-produced things deals with a more comprehensive market. Eventually, the choice in between these 2 sugars can greatly influence flavor profiles and total cooking experiences.
Ecological Influence of Sugar Production
Sugar production, whether from sugar beet or sugar cane, brings substantial ecological implications. Sugar cane farming usually causes deforestation, especially in exotic recommended you read regions, disrupting regional environments and adding to biodiversity loss. The comprehensive use plant foods and pesticides in both sugar beet and sugar cane farming can lead to dirt degradation and water air pollution, impacting bordering habitats and neighborhoods. review Additionally, the high water usage needed for sugar cane watering poses a threat to neighborhood water materials, specifically in arid areas.Alternatively, sugar beet website here farming normally happens in warm environments, which may minimize some logging worries. It is not without its own difficulties, consisting of soil disintegration and dependence on chemical inputs. Generally, the environmental effect of sugar production is diverse, necessitating sustainable farming methods and recognition of resource monitoring to minimize damage to ecological communities and promote ecological health.
Handling Strategies: From Plant to Sugar
Various handling techniques are used to change sugar beet and sugar cane right into granulated sugar, each method reflecting the unique attributes of the source plant. For sugar beets, the procedure begins with cleaning and cutting the origins into thin strips, which are after that subjected to diffusion-- a strategy where warm water extracts sugar from the beet pieces. The resulting fluid is purified, concentrated, and crystallized.In contrast, sugar cane handling includes crushing the stalks to extract juice, complied with by clarification to get rid of contaminations. The juice is after that vaporized, resulting in syrup that goes through condensation. Both procedures are adhered to by splitting up of the sugar crystals from the molasses, which is a by-product. The lasts consist of drying out and packaging the granulated sugar for circulation. These techniques highlight the distinct paths through which these two plants produce sugar, each with its very own set of difficulties and efficiencies.
Economic Facets of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Industries
The economic landscape of the sugar beet and sugar cane sectors reveals notable differences in production prices, market characteristics, and regional influences. Sugar beet, largely grown in warm climates, frequently incurs higher manufacturing prices due to labor and input expenses. On the other hand, sugar cane prospers in exotic regions, normally taking advantage of lower labor prices and positive weather problems, which can lead to greater returns.Market characteristics also vary, as sugar cane dominates international production, representing around 80% of sugar outcome. This occurrence influences prices structures and profession circulations. On the other hand, sugar beet is extra regionally focused, specifically in Europe and North America, impacting regional economic climates dependent on beet production.
Changes in international sugar rates can substantially impact both industries, influencing farmer revenue and investment degrees. Understanding these economic elements is necessary for stakeholders intending to browse the complexities of the sugar market properly.

Often Asked Concerns

Can Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Be Intercropped Successfully?
Intercropping sugar beet and sugar cane provides difficulties as a result of varying growth requirements and environmental demands. With careful administration and ideal problems, it may generate benefits such as enhanced soil health and resource effectiveness.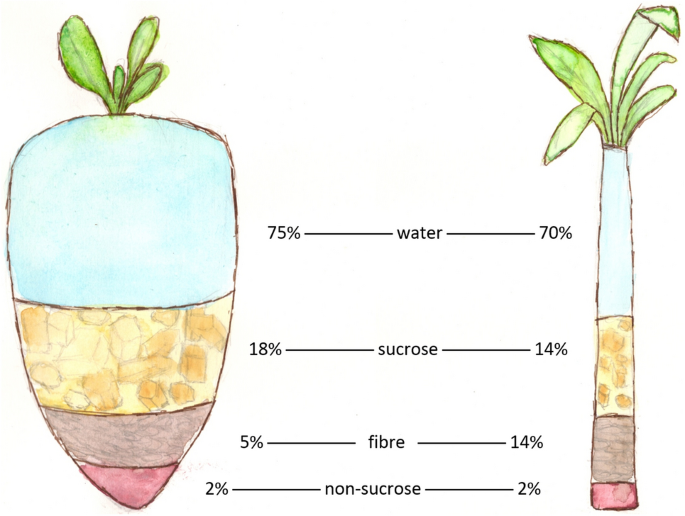
What Are the Historic Origins of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The historic beginnings of sugar beet trace back to 18th century Europe, while sugar cane has roots in Southeast Asia, grown for hundreds of years. Both plants have actually considerably influenced international sugar manufacturing and agriculture.Exactly How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Soil Wellness?
The results of sugar beet and sugar cane on soil health and wellness vary. Sugar beet can improve soil structure and nutrient web content, while sugar cane might diminish nutrients if not taken care of appropriately, impacting long-term dirt fertility.
Exist Any Kind Of Emerging Technologies in Sugar Production?
Arising technologies in sugar production consist of precision farming, progressed genetic modification for greater yields, and innovative extraction methods. These developments aim to improve performance, minimize ecological impact, and boost the general sustainability of sugar manufacturing procedures.What Are the Trick Differences in Labor Demands for Both Plants?
The vital distinctions in labor requirements for sugar beet and sugar cane hinge on planting, harvesting, and processing. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. Sugar beet normally requires more automation, while sugar cane commonly requires extra manual labor for gathering and processing phasesReport this wiki page